The Soil Moisture Sensor is used to measure the water content (volumetric water content) of soil. This makes it ideal for performing experiments in courses such as soil science, agriculture science, environmental science, horticulture, botany, and biology. Use the soil Moisture sensor to:
- The sensor measures the loss of moisture over time due to evaporation and plant uptake.
- It can evaluate optimum soil moisture content for various species of plants.
- It is used to monitor soil moisture content to control irrigation in greenhouses.
- They can enhance your bottle biology experiments.
Must See:
What is Volumetric Water Content?
In very simplified terms, dry soil is made up of solid material and air pockets, called pore spaces (the pore space of soil contains the liquid and gas phases of soil). A typical volumetric ratio of soil would be 55% solid material and 45% pore space.
As water is added to the dry soil, the pore spaces begin to fill with water. Soil that seems damp to the touch might now have 55% minerals, 35% pore space and 10% water. So this would be an example of 10% volumetric water content.
The maximum water content in this scenario will be 45% because at that value all the available pore space has been filled with water. This soil is referred to as being saturated (completely wet) because, at 45% volumetric water content, the soil can hold no more water.
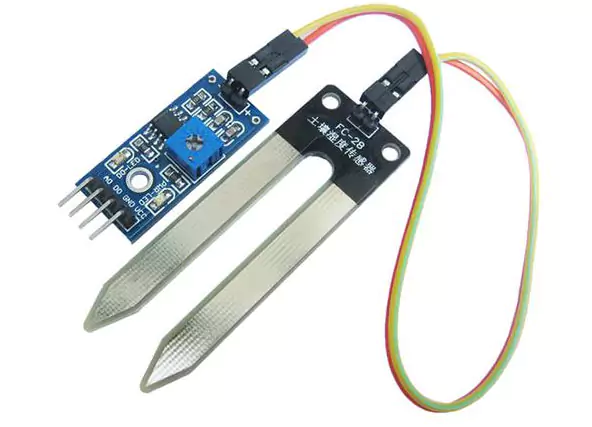
Soil Moisture Sensor Pinout
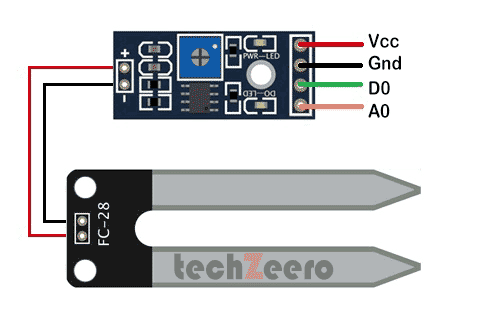
Specifications
| Board Size | 3.2 cm x 1.4 cm |
| Working voltage | 5V DC |
| Working current | <20 mA |
| Interface type | Analog |
| Working Temperature | 10°C~30°C |
How the Soil Moisture Sensor Works
This Sensor uses capacitance (the ability of a system to store an electric charge) to measure dielectric permittivity of the surrounding medium. In soil, the dielectric permittivity is a function of the water content.
The sensor creates a voltage proportional to dielectric permittivity, and therefore the water content of the soil. The Soil Moisture Sensor averages the water content over the entire length of the sensor.
The influence zone is of 2cm with respect to the flat surface of the sensor and at extreme edges, it has little or no sensitivity.
The Soil Moisture Sensor is used to measure the loss of moisture in the soil over time due to evaporation and plant uptake (water used by plants), evaluate optimum soil moisture contents for various species of plants, monitor soil moisture content to control irrigation in greenhouses and enhance bottle biology experiments.